- <GetStart>
- CSPro User's Guide
- The CSPro System
- Data Dictionary Module
- The CSPro Language
- Data Entry Module
- Batch Editing Applications
- Tabulation Applications
- Data Sources
- CSPro Statements and Functions
- Templated Reporting System
- HTML and JavaScript Integration
- Action Invoker
- Appendix
- <CSEntry>
- <CSBatch>
- <CSTab>
- <DataViewer>
- <TextView>
- <TblView>
- <CSFreq>
- <CSDeploy>
- <CSPack>
- <CSDiff>
- <CSConcat>
- <Excel2CSPro>
- <CSExport>
- <CSIndex>
- <CSReFmt>
- <CSSort>
- <ParadataConcat>
- <ParadataViewer>
- <CSCode>
- <CSDocument>
- <CSView>
- <CSWeb>
Importing Data to CSPro Format
There are occasions, such as when using lookup files, when you will want to convert data created in another application to a format that CSPro can read. This is a two-step process:
- Convert the data to a flat file with one record per line and all records for a case organized together. (Read more about data requirements or CSPro's file structure.)
- Create a CSPro dictionary that describes this data file.
There are many formats from which data can be converted, but converting data to CSPro format from Microsoft Excel is the most common task. There is a tool, Excel to CSPro, that can do this automatically for you. It is the preferred way of converting data. It is also possible to create a flat file yourself from within Excel. To convert data to CSPro format:
- Open a file in Excel. We will demonstrate this conversion using the following file:

- Remove any header information in the file. CSPro data files should contain only data and thus any metadata (e.g., column headings) should be removed:

- All fields must be right-justified:

- Remove any specialized formatting attached to cells (unless that formatting is desired in the final output):
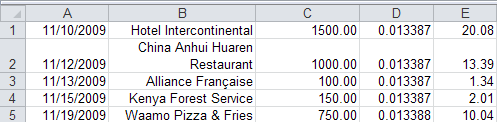
- Set the column widths to appropriate values. When this information is finally saved, the width of each column determines the length of each item in your CSPro dictionary.

- Save As, choosing "Formatted Text (Space delimited) (*.prn)" as the output format:

Using the above example, the resulting file looks like this:
11/10/2009 Hotel Intercontinental 1500.00 0.013387 20.08
11/12/2009China Anhui Huaren Restaurant 1000.00 0.013387 13.39
11/13/2009 Alliance Française 100.00 0.013387 1.34
11/15/2009 Kenya Forest Service 150.00 0.013387 2.01
11/19/2009 Waamo Pizza & Fries 750.00 0.013388 10.04 - Create a CSPro dictionary that describes this data. The length of each item is determined by the column width specified in Excel. Other options, such as whether a decimal character should exist, or whether numeric values should be zero-filled, can also be specified in Excel.
It is a good idea to run frequencies on each item to make sure that the dictionary you created properly describes the .prn file.
The above example is a rather simple one, but more complex imports, including importing cases with multiple records (and thus a record type), are also possible.