- <GetStart>
- CSPro User's Guide
- The CSPro System
- Data Dictionary Module
- The CSPro Language
- Data Entry Module
- Batch Editing Applications
- Tabulation Applications
- Data Sources
- CSPro Statements and Functions
- Templated Reporting System
- HTML and JavaScript Integration
- Action Invoker
- Appendix
- <CSEntry>
- <CSBatch>
- <CSTab>
- <DataViewer>
- <TextView>
- <TblView>
- <CSFreq>
- <CSDeploy>
- <CSPack>
- <CSDiff>
- <CSConcat>
- <Excel2CSPro>
- <CSExport>
- <CSIndex>
- <CSReFmt>
- <CSSort>
- <ParadataConcat>
- <ParadataViewer>
- <CSCode>
- <CSDocument>
- <CSView>
- <CSWeb>
Encrypted Data
Overview
Using the Encrypted CSPro DB data source, you can read from and write to a data file that is protected by a password. The file cannot be opened without the password, meaning that it is important to implement a sufficient password management policy to ensure that you do not lose data during the data collection process.
An Encrypted CSPro DB data source is like a CSPro DB data source and can be used in any CSPro application. The only difference is that, upon opening the file, CSPro requires the specification of a password. There are two ways to specify a password:
Password entry: A dialog box will appear allowing the user to enter the password. The password must be at least four characters. If the data file does not exist and is being created for the first time, the user must enter the password twice to ensure that the password is entered correctly. You can reduce the number of times that a user must enter the password by allowing the password to be cached for a specified duration on the machine. When opening an existing file, if the password is not correct, the user will be prompted to enter the password again.
Connection string: The password can be specified in a connection string used in a PFF file or by setfile. If the password is specified in the connection string, then the user will not be prompted to enter a password. If the data file does not exist and is being created for the first time, the specified password will be used to encrypt the file. When opening an existing file, if the password is not correct, the opening of the file will fail. For example, the following connection string opens the file pilot-data.csdbe with the password jiw~d_fpF9.
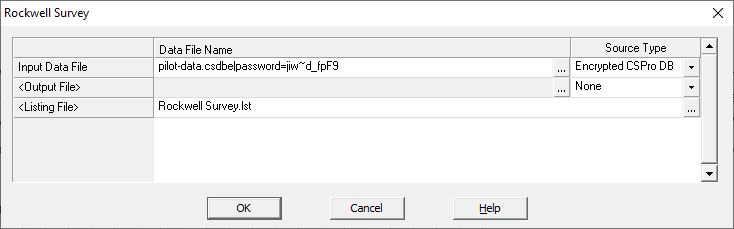
While the data in the file is encrypted, it is also a good idea:
- To encrypt the entire drive where the CSPro application and data files reside, using encryption such as Windows BitLocker or Android's full-disk encryption.
- Not to store passwords in plaintext anywhere (such as in a CSPro logic file or in a PFF file, as is done in the above image).
- To synchronize your data using a secure protocol (such as CSWeb over https). If you encrypt your data file on a tablet but then transfer the data over http using syncdata, that defeats much of the purpose of encrypting.
Technical Details
Encrypted CSPro DB files are SQLite files encrypted using the SQLite Encryption Extension (SEE) using "AES-256 in OFB mode." The specified password is not used as the key input to SEE but is instead hashed to create a 256-byte key that is used to encrypt the file. If allowed, this hash, not the password, is cached on the machine. A fixed salt is used during the hashing process because there is no suitable place to store a dynamic salt. This means that the same password will always result in the same encryption key.